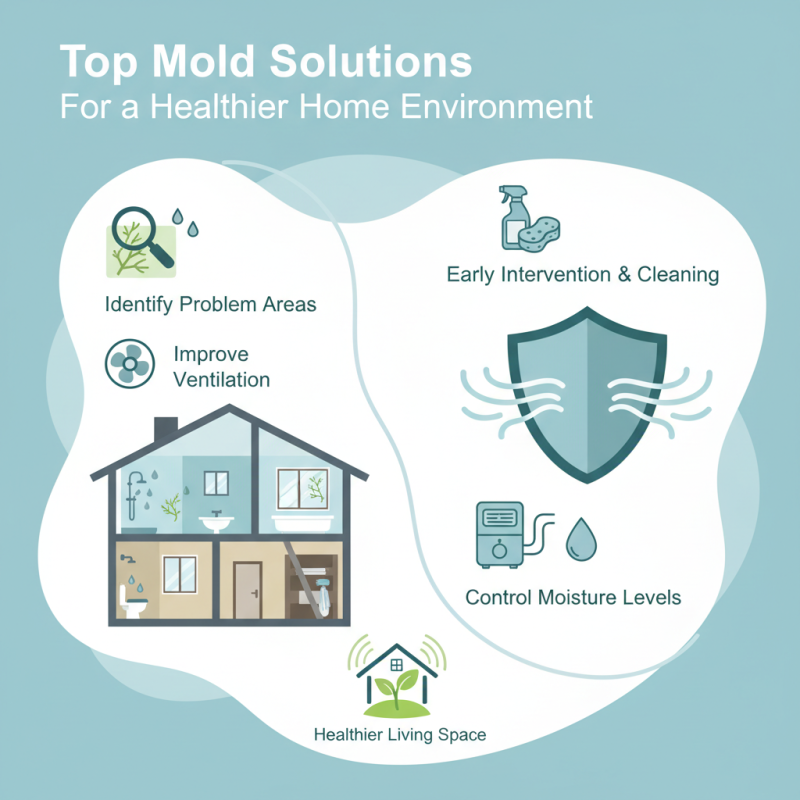
In today's pursuit of a healthier home environment, understanding the significance of effective mold solutions has never been more crucial. As homes age and the prevalence of moisture increases, the demand for professional insight on mold prevention and remediation grows. Leading mold expert Dr. Emily Turner emphasizes the importance of early intervention, stating, “Implementing the right mold solution at the first signs of growth can safeguard not only the structure of your home but also the health of its inhabitants.”
With countless families grappling with allergies, respiratory issues, and other health concerns linked to mold exposure, it is imperative to explore actionable strategies that can help maintain a safe living space. From identifying potential problem areas to utilizing specific mold solutions, this guide will equip homeowners with the necessary knowledge to combat mold efficiently, ensuring a cleaner and healthier environment for everyone. We will delve into the essential practices and emerging technologies that stand at the forefront of mold remediation efforts, empowering individuals to take proactive steps in their homes.
Mold is not just an unsightly nuisance; it has significant implications for home health. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), exposure to mold can trigger respiratory problems, allergic reactions, and even more severe health issues in vulnerable populations, particularly children, the elderly, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions. A report from the World Health Organization (WHO) also indicates that indoor mold growth can increase the risk of respiratory infections, making a healthy home environment even more critical.
To mitigate the impact of mold, it is essential to maintain optimal humidity levels in your home. A humidity level between 30% and 50% is often recommended to inhibit mold growth. Regularly checking for leaks and promptly addressing any water damage is crucial. Simple actions, such as using exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens, can help reduce moisture levels. Furthermore, the American Lung Association suggests that proper ventilation in living spaces promotes air circulation, decreasing mold spores.
Tips: Incorporate plants known for their air-purifying qualities, such as spider plants or peace lilies, which may help improve indoor air quality. Additionally, consider regularly inspecting areas prone to dampness, like basements and crawl spaces, and be proactive in using mold-resistant materials during home improvement projects. By taking these steps, homeowners can significantly reduce the health risks associated with mold.
Mold is a common issue in residential environments, and understanding the types of mold that can proliferate indoors is key to maintaining a healthier home. Among the varieties most often encountered, *Aspergillus* is prevalent in homes, thriving in warm, damp areas such as basements and showers. A report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicates that this mold can produce allergens and irritants that may lead to respiratory issues in sensitive individuals.
Another type of mold frequently found indoors is *Stachybotrys chartarum*, commonly referred to as black mold. This mold requires moisture to grow and can often be found on materials with a high cellulose content, such as drywall and wood. According to a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, exposure to black mold can significantly contribute to respiratory problems and is especially concerning for individuals with asthma or weakened immune systems.
Finally, *Cladosporium* is another mold type often encountered in both indoor and outdoor environments. It can grow on various surfaces, including fabrics and wooden materials, usually where moisture is present. Data from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) suggests that while *Cladosporium* is less harmful than others, prolonged exposure can still trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate asthma conditions. Recognizing and addressing these common mold types is crucial for creating and maintaining a safe and healthy living space.

Mold is a persistent problem in many homes, often thriving in damp and poorly ventilated areas. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), mold can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems and allergic reactions. To mitigate these risks, homeowners must adopt effective mold prevention strategies. One of the primary methods is controlling moisture levels in the home. The EPA suggests that keeping indoor humidity below 60% can significantly reduce mold growth. Use dehumidifiers in damp areas like basements and ensure proper ventilation in bathrooms and kitchens to help combat excess moisture.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the home are also crucial in mold prevention. The CDC reports that conducting frequent checks for leaks in plumbing and roofing can help identify potential problem areas before they become a significant issue. Additionally, homeowners should ensure that gutters and downspouts are functioning correctly to direct water away from the foundation, minimizing the likelihood of water accumulation. By taking these proactive steps, homeowners can create a healthier living environment and effectively reduce the chances of mold proliferation in their homes.
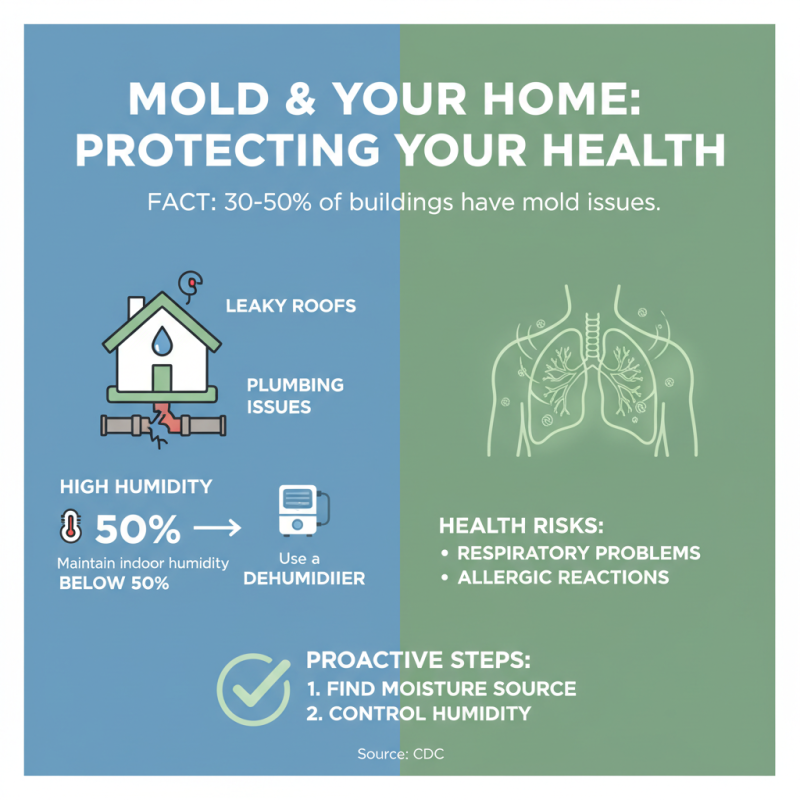
Mold growth in homes can lead to serious health issues, including respiratory problems and allergic reactions. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 30% to 50% of all buildings may have mold problems, making it essential for homeowners to take proactive measures. The first step in effective mold removal is to identify the source of moisture, as mold thrives in damp environments. This could range from leaky roofs and plumbing issues to high humidity levels. Homeowners are advised to maintain indoor humidity below 50% and use a dehumidifier in areas prone to moisture accumulation.
Once moisture sources are addressed, the next critical step is mold removal. For small areas, using a mixture of water and detergent can effectively eliminate mold. It's important to wear protective gear, including gloves and masks, to prevent exposure to mold spores. For larger infestations, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends consulting professionals who are certified in mold remediation. This ensures that mold is not just cleaned but also properly contained and disposed of, thereby preventing spores from spreading to unaffected areas. Regular inspections and maintenance, paired with these steps, can help maintain a healthier home environment, significantly reducing the risks associated with mold exposure.
When dealing with mold in your home, knowing when to seek professional help is crucial for maintaining a healthy living environment. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), mold can grow in as little as 24 to 48 hours in areas with excessive moisture. As mold spores proliferate, they can significantly affect indoor air quality, causing respiratory issues and other health problems, particularly in sensitive populations such as children and individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Homeowners should be vigilant and consider seeking professional intervention when they encounter significant mold growth—typically characterized by patches larger than a few square feet—or when mold recurs despite remediation efforts. The National Institute of Health (NIH) reports that exposure to mold can lead to symptoms ranging from allergic reactions to chronic respiratory conditions, reinforcing the importance of timely professional assessment.
Furthermore, specialists use advanced diagnostic tools to identify hidden mold in areas that are not easily visible, such as behind drywall or within HVAC systems, ensuring comprehensive treatment that DIY methods often cannot achieve.