Industrial molding is a fundamental process that plays a crucial role in various manufacturing sectors. As businesses strive for efficiency and innovation, understanding the different industrial molding processes becomes essential for success. This article explores the top 10 industrial molding techniques that every professional should know. Each method brings unique advantages and fits different application needs, impacting everything from product design to production speed.
With a keen focus on sustainability and cost-effectiveness, manufacturers are increasingly adopting advanced molding techniques to meet market demands. The significance of mastering these industrial molding processes cannot be overstated, as they are key to optimizing production workflows and enhancing product quality. Whether you are involved in automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, or any other industry, a solid grasp of these processes will empower you to make informed decisions that drive growth and competitiveness. Join us as we delve into the most essential industrial molding processes that can elevate your operations and ensure long-term success.

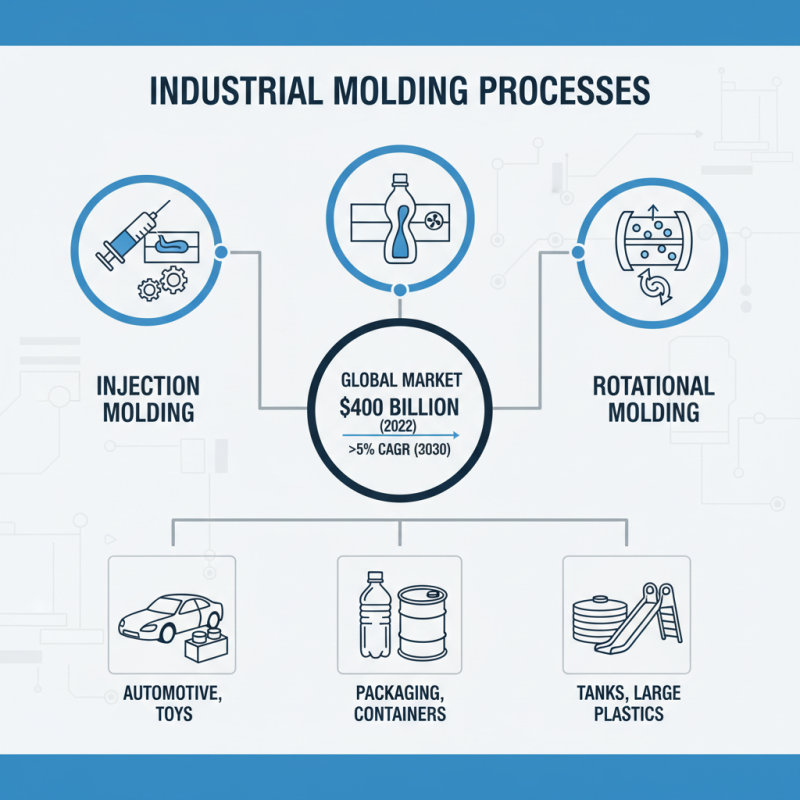
Industrial molding processes play a pivotal role in various manufacturing sectors, enabling the mass production of complex shapes and components with precision and efficiency. In 2022, the global market for industrial molding was valued at approximately $400 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5% through 2030. This growth underscores the importance of understanding the different molding techniques available, such as injection molding, blow molding, and rotational molding. Each method presents unique advantages that cater to specific application needs, allowing industries to tailor their production processes effectively.
The significance of mastering these molding technologies cannot be overstated. For instance, injection molding, one of the most widely utilized processes, accounts for nearly 30% of the total plastic production worldwide. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in the automotive and consumer goods sectors is driving advancements in molding technologies. As manufacturers experience pressure to improve production rates and reduce costs, investing in innovative molding processes can lead to competitive advantages. Hence, a comprehensive understanding of these processes is essential for industry professionals aiming for success in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Injection molding is a highly efficient and widely used manufacturing process, primarily employed for producing plastic parts and components. The fundamental principle behind injection molding involves heating plastic pellets until they melt, then injecting the molten material into a mold under high pressure. This method allows for intricate designs and high precision, making it ideal for mass production. One of its key characteristics is the ability to produce complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing techniques.
The versatility of injection molding extends across various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices. Its applications range from small, detailed components to larger structural parts. One significant advantage of injection molding is its scalability; once a mold is created, it can be used repeatedly to manufacture thousands of identical parts efficiently. Additionally, advancements in materials and technology, such as the use of biodegradable plastics and improved energy efficiency, are enhancing the sustainability of injection molding processes. By understanding the principles and advantages of injection molding, manufacturers can leverage this technique to drive productivity and innovation in their operations.
Blow molding is a prominent manufacturing process used to produce hollow plastic parts, widely utilized in various industries for its efficiency and versatility. This technique involves heating thermoplastic materials until they become pliable, followed by forming them into the desired shape using pressure. The process typically begins with melting plastic pellets, which are then extruded into a parison—a tube-like structure. This parison is inflated using air, expanding it to fit the mold. As the plastic cools, it takes on the mold's shape, resulting in a functional and lightweight hollow part.
When engaging in blow molding, certain tips can enhance product quality and process efficiency. First, it's essential to carefully select the proper resin and adjust the processing parameters based on the material characteristics. Understanding the thermal properties of the chosen plastic can significantly impact the finished product's durability. Additionally, regularly maintaining molds and machinery ensures consistent performance and reduces production downtime.
Another critical aspect of blow molding is the design of the part itself. Incorporating features such as thicker walls at stress points can improve strength, while lightweight designs can reduce costs and enhance usability. Properly analyzing product requirements during the design phase can lead to better performance and greater customer satisfaction. Overall, applying these techniques not only streamlines the manufacturing process but also results in high-quality plastic parts that meet market demands.
Rotational molding is an innovative manufacturing process widely used in the production of hollow plastic parts. This method involves heating a mold while it is rotated on two axes, allowing the molten material to coat the inside of the mold evenly. One of the primary advantages of rotational molding is its ability to create complex shapes with a uniform wall thickness, making it ideal for custom designs. This process is particularly favored in industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods, where durability and precision are paramount.
When considering rotational molding for your project, it’s essential to focus on the design phase. Make sure to utilize CAD software to visualize your product and optimize mold flow. Additionally, selecting the right material is crucial; options like polyethylene and nylon provide excellent strength and flexibility.
Tips for success include fully understanding the capabilities of the process. For example, designing for rotational molding usually requires thicker walls, so be sure to account for that in your design specifications. It is also beneficial to work closely with experienced manufacturers who can advise on design modifications that improve function while reducing production costs. This collaborative approach can lead to inventive designs that stand out in the marketplace.
This bar chart illustrates the various advantages of rotational molding rated on a scale from 1 to 10. Key benefits include cost efficiency, design flexibility, and material efficiency, making it a popular choice for custom designs in various industries.
Thermoforming is a widely utilized industrial molding process for creating plastic components with precision and efficiency. The process begins with the selection of a suitable thermoplastic sheet, which is then heated until it becomes pliable. Once the material has reached the desired temperature, it is draped over a mold that represents the shape of the final product. This stage is critical, as the uniformity of the heating affects the quality of the finished component.
After the sheet is positioned, a vacuum or pressure is applied to mold the material closely against the surface of the mold. This ensures that all details of the mold are captured in the formed plastic. Once the cooling phase is complete, the rigid part can be removed from the mold. Thermoforming is particularly favored for its ability to produce lightweight and cost-effective parts, making it ideal for various applications in industries ranging from packaging to automotive. Proper understanding of the process steps involved is essential for achieving optimal results and enhancing product performance.






