Injection molding products play a pivotal role in contemporary manufacturing industries, revolutionizing the way components are produced across various sectors. This versatile technique involves the process of injecting molten material into a mold, allowing for the creation of intricate and precise designs at high volumes. As industries strive for efficiency and cost-effectiveness, injection molding has emerged as a preferred method for producing everything from consumer goods to automotive parts, contributing significantly to mass production outcomes.
The impact of injection molding products extends beyond mere manufacturing capabilities; they catalyze advancements in design and innovation. The ability to produce complex geometries with exceptional accuracy not only enhances product quality but also paves the way for new applications and functionalities. Furthermore, the efficiency of the injection molding process leads to reduced waste and lower energy consumption, aligning with the industry's growing emphasis on sustainability. As manufacturers continue to adopt this technology, understanding the implications and benefits of injection molding products becomes essential for staying competitive in today's dynamic market landscape.

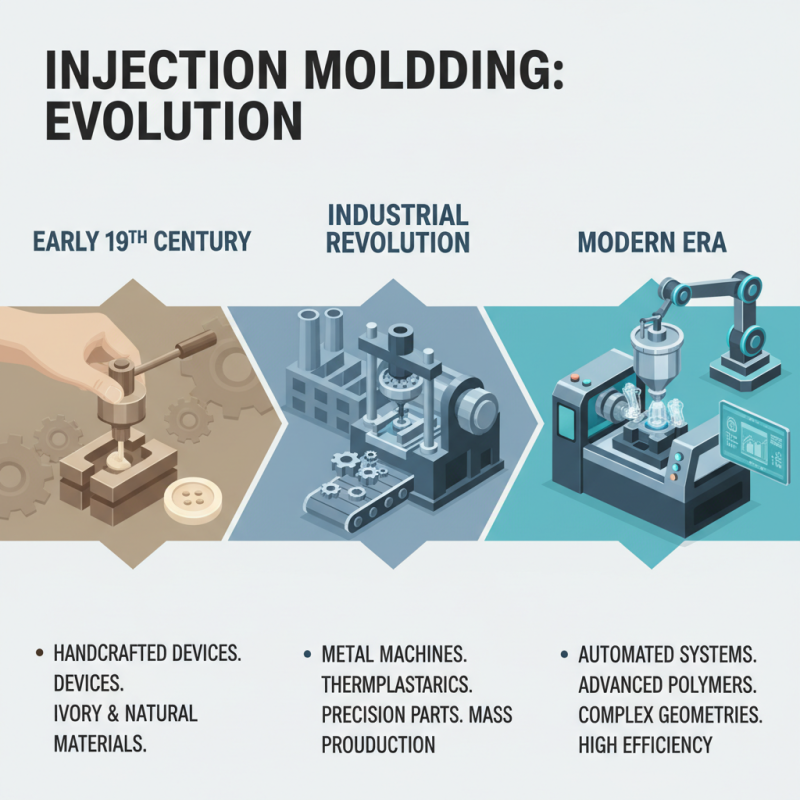
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 19th century. Initially, the technique began with simple, handcrafted devices made from materials like ivory. As technology advanced, the process transitioned to using metals and thermoplastics, leading to the rapid development of machinery capable of producing intricate shapes with high precision. This evolution was propelled by needs arising from the industrial revolution, which demanded efficient and reliable manufacturing methods to meet the growing consumer market.
Throughout the 20th century, injection molding saw substantial innovations in equipment and techniques, enhancing its versatility and efficiency. The introduction of automatic feed systems, temperature-controlled environments, and advanced computer-aided design (CAD) has allowed for more complex and diverse product designs. This historical development has not only improved the accuracy of molded products but has also significantly reduced production times and costs. Consequently, injection molding has become a cornerstone in various manufacturing industries, impacting the way products are designed and produced, from automotive components to consumer goods, shaping the landscape of modern manufacturing.
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that relies on various materials, each with distinct properties that significantly influence the final product. The most commonly used materials in injection molding include thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, and elastomers. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global thermoplastic resin market is projected to grow to over 96 million tons by 2024, driven largely by the automotive and consumer goods sectors.
Thermoplastics, such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), are favored for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and recyclability. These materials can be reheated and reshaped, making them ideal for complex designs and high-volume production. On the other hand, thermosetting plastics, such as epoxy and phenolic resins, provide superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for applications that require durable and stable products.
Elastomers, known for their flexibility and resilience, are also commonly used in injection molding for applications like seals and gaskets. The diverse properties of these materials allow manufacturers to tailor their products to meet specific performance requirements. A study by Allied Market Research indicates that the global demand for elastomers is expected to reach $73 billion by 2025, highlighting their critical role in various industries, from automotive to healthcare. By selecting the appropriate material, manufacturers can not only improve product performance but also drive innovation in design and functionality.
The process of injection molding encompasses several critical steps that transform a concept into a tangible product. Initially, it starts with designing the part, where engineers use CAD software to create detailed models ensuring the product meets specifications. Once the design is finalized, creating the mold is the next step. This often involves machining or 3D printing to craft a cavity that will define the shape of the final product. The precision in this stage is vital, as even minor errors can lead to significant issues in production.
After the mold is completed, the actual injection molding process begins. Thermoplastic pellets are heated until they melt and then injected into the mold under high pressure. This stage is crucial, as it requires precise temperature control and timing to achieve a quality finish. Upon cooling, the mold is opened, and the solidified product is ejected. Finally, any additional processes such as trimming or assembly may be performed to prepare the product for distribution.
Tips: When designing for injection molding, consider the accessibility of features to ensure easy manufacturing. Additionally, keep in mind the material shrinkage upon cooling to avoid dimensional issues. Collaborative planning with engineers during the design phase can significantly enhance efficiency in later stages of production, ensuring that potential challenges are addressed early on.
Injection molding is a pivotal manufacturing process that has revolutionized various industries by enhancing production efficiency and driving down costs. According to the 2021 "Global Injection Molding Market Report", the efficiency of injection molding can be attributed to its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision at scale. This technique allows manufacturers to mass-produce components, reducing lead times significantly. The report indicates that companies often see a production increase of up to 30% when employing advanced injection molding technologies, which can play a critical role in meeting market demands swiftly.
Furthermore, cost reduction is another substantial benefit linked to injection molding. The process minimizes material waste due to its high accuracy and repeatability. According to industry studies, manufacturers can reduce material costs by approximately 15-20% compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, the automation capabilities inherent in modern injection molding machinery help decrease labor costs and improve overall factory output. A survey conducted by the Society of Plastics Engineers revealed that 78% of manufacturers reported reduced operational costs after implementing injection molding processes, underlining its significance in optimizing production and enhancing profitability.
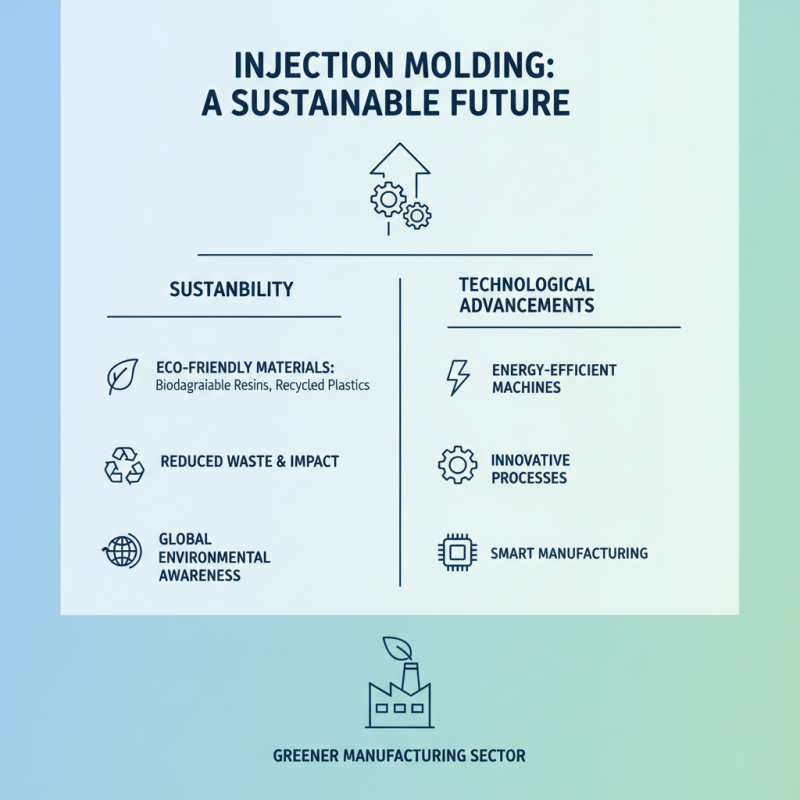
The injection molding industry is rapidly evolving, with sustainability and technological advancements taking center stage in shaping its future. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce waste and environmental impact. Biodegradable resins, recycled materials, and energy-efficient molding machines are gaining popularity in an industry that once heavily relied on traditional plastics. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, companies are motivated to innovate, ensuring their practices align with sustainable principles, ultimately leading to a greener manufacturing sector.
Tip: When considering sustainability in injection molding, explore partnerships with suppliers who prioritize recycled materials and green technologies. This not only enhances your brand's image but also reduces costs associated with waste management and material sourcing.
Technological advancements, such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT), are revolutionizing injection molding processes. These innovations allow for greater precision, automation, and real-time monitoring of production, leading to reduced cycle times and improved quality control. By integrating smart technologies, manufacturers can streamline operations and reduce downtime, enhancing overall efficiency. Additionally, advancements in simulation software enable better design and material usage, minimizing waste before the production phase even begins.
Tip: Invest in training for your workforce to ensure they are adept at using new technologies in injection molding. Skilled employees are key to leveraging these advancements effectively, helping your business stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.