Low pressure injection molding is transforming the manufacturing landscape. This technique is gaining traction for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Industry expert John Smith once said, "Low pressure injection molding offers precision with reduced waste." This insight highlights the growing demand for sustainable manufacturing practices.
Low pressure injection molding uses less force during the molding process. This results in lower energy consumption. It also minimizes the risk of damaging delicate components. Many companies are adopting this technique to enhance product quality while cutting costs. However, challenges remain. Not all materials are suitable for low pressure applications. Manufacturers must carefully select materials that retain their properties under lower pressures.
The potential for innovation is immense. As technology evolves, we may see newer applications for low pressure injection molding. Not all businesses have fully embraced this shift. Some still rely on traditional methods, which can lead to inefficiencies. Reflecting on these gaps can help the industry move forward.

Low pressure injection molding has gained popularity in various industries. The technique is known for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. In this process, lower pressure is utilized, resulting in reduced stress on materials and molds. This leads to fewer defects and higher-quality products. One notable aspect is the versatility of materials that can be used. Both thermoplastics and thermosets can be molded effectively, which opens doors for creative possibilities.
However, it is essential to be aware of the limitations. While low pressure methods are beneficial, they may not be suitable for all applications. Certain designs require higher pressures to achieve finer details. The mold design itself plays a crucial role in the success of low pressure injection molding. If a mold is poorly designed, the final product may suffer from imperfections like surface defects. It's a balancing act between pressure, temperature, and timing.
Additionally, the process speed can be slower compared to traditional methods. This might lead to longer production times, which can be a concern for manufacturers on tight schedules. Constant reflection on the efficiency of the setup and troubleshooting any inconsistencies is vital. Ultimately, understanding these techniques allows for better decision-making in production. This can lead to enhanced product development and more satisfied customers.
| Technique | Pressure Range (psi) | Material Compatibility | Cycle Time (seconds) | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas-Assisted Injection Molding | 1,000 - 3,000 | Thermoplastics, Elestomers | 30 - 120 | Reduced material usage, complex shapes |
| Low Pressure Injection Molding | 10 - 1,000 | Engineering Plastics | 40 - 150 | Lower energy consumption, better surface finish |
| Injection-compression Molding | 500 - 2,000 | Polycarbonate, PMMA | 25 - 100 | Higher precision, lower cycle time |
| Two-component Injection Molding | 500 - 2,500 | Multiple Thermoplastics | 60 - 180 | Cost-effective for complex parts |
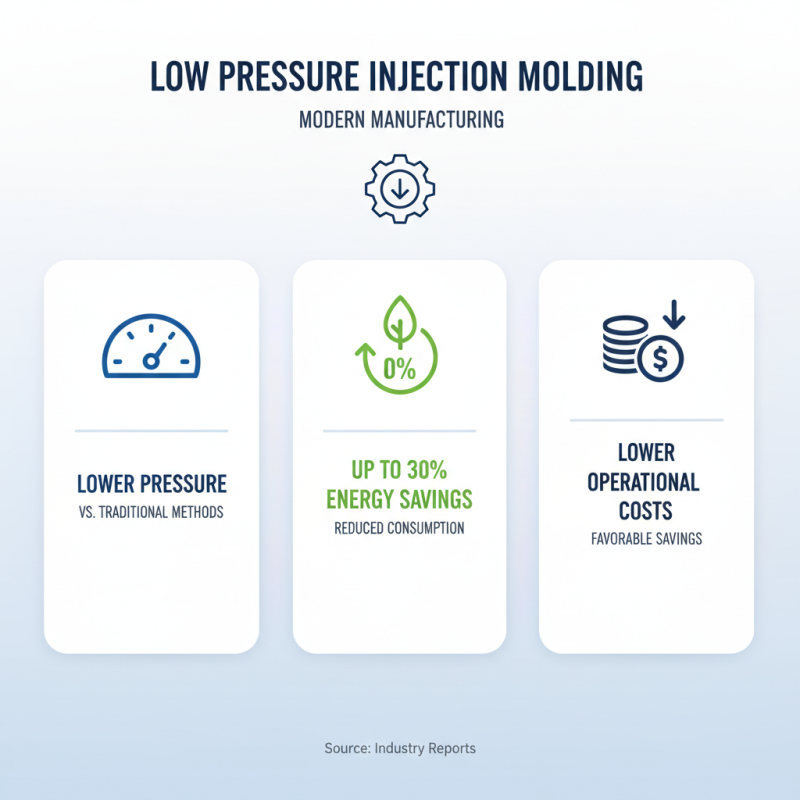
Low pressure injection molding is gaining traction in modern manufacturing. This technique uses lower pressures compared to traditional methods. Reports suggest that this can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. Favorable energy savings often translate to low operational costs for manufacturers.
One significant advantage of low pressure injection molding is reduced material waste. With control over the injection process, manufacturers can minimize excess material. Studies indicate that waste reduction can improve profitability by around 15%. Moreover, the enhanced precision often results in better part quality. Fewer defects mean less rework, saving both time and resources.
However, low pressure processes are not without challenges. It may struggle with certain complex designs. Engineers often face limitations with high-viscosity materials. This could lead to potential compromises in product durability. Each project requires careful consideration of these factors. Manufacturers must weigh the benefits against possible drawbacks. The evolving landscape of injection molding invites ongoing evaluation.
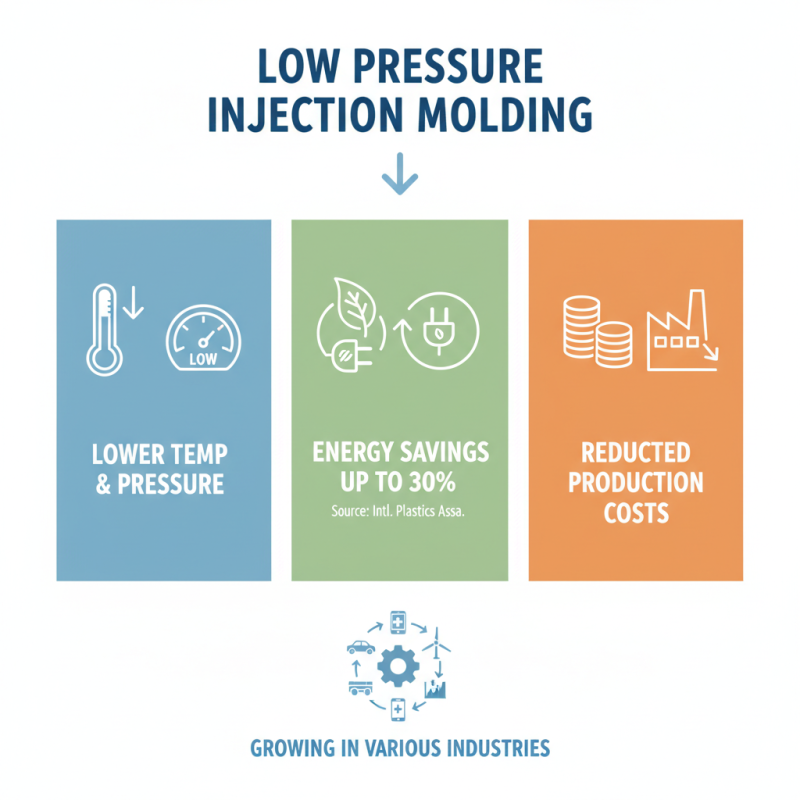
Low pressure injection molding is becoming increasingly popular in various industries. This technique uses lower temperatures and pressures than traditional methods. It reduces energy consumption by up to 30%, according to a report by the International Plastics Association. This significant reduction makes a positive impact on production costs.
Key components of low pressure injection molding machines include the injection unit and the clamping unit. The injection unit must be precise. It determines how material flows into the mold. Commonly, screw designs can vary. This variation can affect the melt quality. A poorly functioning injection unit may result in defects, leading to costly rework.
The clamping unit holds the mold in place during injection. Its design is critical for effective material containment. Hydraulic systems often provide the necessary force. However, they can be less energy-efficient. Companies must evaluate design choices. Balancing cost and performance remains a challenge. Data from industry reports show that advancements in materials and machine designs can further enhance efficiency. However, adaptability in machine setup is essential. Lack of proper adjustments can greatly affect production quality and timing.
Low pressure injection molding is gaining popularity in various industries. It offers advantages like lower energy consumption and reduced waste. Understanding the steps in this process is crucial for optimal results.
Step 1: Material Preparation
The process begins with material preparation. Thermoplastic pellets are fed into the machine. Then, they are heated until they reach a molten state. The heating must be precise. Overheating can degrade the material. Next, the molten plastic enters the mold under low pressure. This pressure prevents defects but requires careful control. It's easy to overlook details here.
Step 2: Cooling
Cooling is the next crucial step. The mold needs time to solidify the part. Too little time can lead to warping. Conversely, excessive cooling may prolong production. As the part cools, it's ejected from the mold. The design of the ejection mechanism is important. It should avoid damage to the final product. Fine-tuning these steps leads to improved efficiency and quality in low pressure injection molding. However, achieving perfection is always a challenge.
Low pressure injection molding is gaining attention. It offers several benefits when compared to traditional methods. One notable advantage is reduced energy consumption. The process requires less force, leading to lower operating costs. Additionally, it often results in less stress on materials. This can translate into stronger, more durable parts.
However, the technique has its limitations. Parts produced may exhibit less precision than those made with traditional methods. Some complex geometries might not be achievable. This brings us to the question of applications. Low pressure techniques work well for specific materials and products. Traditional processes still dominate sectors requiring high accuracy and fine detail.
Understanding these nuances is crucial. Evaluating project needs is essential for choosing the right method. For some projects, the speed of production could be an issue. Low pressure techniques may take longer to set and cure. This reflection is vital for optimizing manufacturing choices.